Blockchain feasibility study in india
Produced by Lai Pandey
Introduction
This wiki project provides an introduction to the transformative potential of blockchain technology in India. Blockchain, a decentralized and immutable digital ledger, enables secure and transparent transactions, revolutionizing various industries with its trust, transparency, and efficiency. The study focuses on widespread blockchain adoption across diverse sectors, the emergence of Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs), and the practical applications and future prospects of blockchain in the Indian economy.
To gain insights into blockchain adoption in India, a comprehensive survey was conducted among companies across sectors. The survey aimed to understand their experiences, challenges, and perceived benefits in implementing blockchain solutions. Through analysis of survey findings, this research highlights the current state of blockchain adoption and provides valuable insights into opportunities and obstacles faced by industry players.
Throughout the research, several key questions are explored. What does the future hold for blockchain technology in India? How can different sectors harness its transformative power for growth and innovation? Which sectors are poised for significant blockchain adoption? By addressing these questions, this research provides insights into the trajectory of blockchain in India and its impact on sectors like finance, supply chain, and healthcare.
Additionally, it also includes a compelling case study of a specific company. By employing financial forecasting techniques, the case study examines the growth rate and predicts the financial performance. This real-life application of blockchain technology offers a tangible example of its potential impact on business growth.
Moreover, readers gain an understanding of the challenges and opportunities associated with implementing blockchain solutions in India. The research delves into the regulatory landscape, unique business challenges, and potential benefits that blockchain brings to the Indian economy and society.
By examining survey findings, analyzing the case study, and exploring broader implications, this research equips readers with knowledge to navigate the evolving blockchain landscape in India. It offers insights into driving factors behind blockchain adoption, sectors with growth potential, and implications for businesses and the Indian economy.
Development of Blockchain in India
Origin of Blockchain in India
Blockchain Technology has emerged as a revolutionary concept in recent years and has garnered considerable attention worldwide, including in India. The trend of Blockchain Technology started in India started around 2016 when Bitcoin and other cryptocurrencies gained popularity. The concept of Blockchain, which is the underlying technology behind cryptocurrencies was introduced to India as an innovative and decentralized way of exchanging value without the need for intermediaries.
In 2017, the government of India established a task force to explore the potential of Blockchain technology and create a regulatory framework for the industry. This led to the creation of the IndiaChain project. The IndiaChain project, aimed to create a blockchain-based platform for the exchange of information and services between different government agencies. This helped in promoting the startups, corporates and government agencies exploring the potential of the technology.
The interest in Blockchain in technology grew, and in 2018, the government of Andhra Pradesh (One of the IT hubs of India), planned to build a blockchain ecosystem in the state. The development of IndiaChain, the launch of the National Strategy on Blockchain, and the partnership between the government of Telangana (a potential IT state) and Tech Mahindra to develop a blockchain district have all contributed to the growth of the industry in India to develop a Blockchain district have all contributed to the growth of the industry in India.
Challenges of Blockchain in India
Despite its immense potential, Blockchain technology in India is still in its nascent stages, and there, are several challenges that need to be addressed. We can address these issues into three major domains of Technical Issues, Security issues and Infrastructural issues.
Technical issues The scalability of Blockchain technology has been a big concern for the Indian government. As we know, Blockchain Technology relies on a distributed network of nodes to reach consensus which can sometimes result in slower transaction processing times compared to the traditional systems. With the growing number of transactions and users increase, it will impact the performance and efficiency of the network.
Blockchains could be isolated from each other, and achieving interoperability between different blockchain platforms can be challenging. This can result in limitations in exchanging data and value across different blockchain systems in India.
Infrastructural Issues The major issue is the Talent issue as there is a shortage of skilled professionals in this field. This has created a talent gap that hinders the development of blockchain solutions and limits the growth of the industry.
The other infrastructural issue is it energy consumption. Some blockchain networks, such as those that use of Proof of Work (POW) consensus algorithms, can be energy-intensive, requiring significant computing power and electricity. This can result in environmental concerns and may pose challenges in terms of energy consumption and sustainability in India, where energy resources are sometimes limited.
Security Issues There is Regulatory uncertainty around the blockchain environment in India in its early stages. There is a lack of clarity and regulatory frameworks governing blockchain technology. This has created uncertainty for business looking to adopt blockchain technology. Issues related to data privacy, smart contracts, and digital identity may need to be addressed to provide a conducive regulatory environment for blockchain technology in India. Other security concerns are that the agencies that have adopted Blockchain technology have been a target of cyber-attacks in the past. This has created security concerns and a lack of trust in blockchain technology among some stakeholders.
Major Developments Post- G20 summit
What is G20 summit and why is it important? The G20 summit is an annual meeting of the Group of Twenty (G20), a group of 20 major economies in the world. It provides a platform for leaders from these countries to come together and discuss and coordinate on various economic, financial, and global governance issues. The discussions cover a wide range of topics, such as global economic growth, trade, financial stability, sustainable development, climate change, and other pressing issues. The G20 summit has become a key forum for global economic governance, and its outcomes and declarations can have significant implications for global economic policies and the international financial system.
It has the potential to have a huge impact on the global economy, affecting problems such as economic growth, trade, financial stability, and investment. Policy implications: The G20 summit's decisions and pronouncements have the potential to impact global economic policy and shape international financial rules. Inclusion: Because the G20 comprises both established and emerging economies, discussions on a wide variety of economic and development topics can take place. Setting the global agenda: The G20 frequently considers rising global issues such as climate change, cybersecurity, and other challenges that necessitate collective action.
G20 summit effect on Blockchain Technology in India As India takes over the presidency of the G20 Leaders' Summit for a year, from 1 December 2022 to 30 November 2023, it intends to discuss crypto regulations with member countries such as France, Germany, Russia, the United Kingdom, the United States, China, Russia, and Canada, among others.
Indian Finance Minister Nirmala Sitharaman disclosed the government's intentions for cryptocurrency laws. She indicated that cryptocurrency would be on the agenda of India's G20 presidency, and that the nation plans to develop standard operating procedures (SOPs) for cryptocurrencies. Further, the Finance minister shared that India would like to bring up the topic of crypto assets for debate at the G20 summit, which would pave the way for global countries to have a technology-driven regulatory framework.
Blockchain is a distributed ledger system that enables decentralized, transparent, and secure record-keeping. It has the potential to disrupt a wide range of sectors, including banking, supply chain management, healthcare, and many more. Here's how India, as a G20 member, has become involved in the blockchain: India has taken part in G20 negotiations on policy and regulatory frameworks for blockchain technology. This includes conversations on consumer protection, data privacy, cybersecurity, and financial stability. India has taken the initiative to create its own regulatory framework for blockchain technology to stimulate innovation while mitigating possible hazards.
India has been a prominent participant in international cooperation on blockchain technology through the G20 and other forums. This includes collaboration on research and development, sharing best practices, and policy and regulatory coordination. To share its experiences and learn from other countries, India has also participated in efforts such as the G20 Insights Platform and the G20 Global Smart Cities Alliance on Technology Governance.
India recognizes blockchain's potential to drive economic growth, promote financial development, and improve public-sector services and has been proactive in developing its own policy and regulatory frameworks in this area.
DAOs in India
Challenges of setting up DAOs in India
Decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs) in India encounter various challenges, encompassing both technical and infrastructural aspects. Technical hurdles include the need for improved scalability of blockchain networks to enhance transaction processing speed and capacity, ensuring smart contract security against vulnerabilities and coding errors, achieving interoperability with other systems, and implementing robust privacy and data protection measures. On the infrastructural front, limited or unreliable internet connectivity, especially in certain regions, poses a barrier to seamless participation in DAOs. To overcome these challenges, a collaborative approach is required, involving technological advancements, regulatory clarity, enhanced internet access, and educational initiatives to create an enabling environment for the successful establishment and operation of DAOs in India
Current status of DAOs in India
In the realm of Indian startups, the conventional centralized decision-making process is being disrupted by the emergence of decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs). Bengaluru-based blockchain firm Polygon (formerly Matic Network) has taken a pioneering step by announcing the development of the first DAO of India, allowing communities of users to make transparent decisions through blockchain transactions.
Polygon recognizes the potential of DAOs within its DeFi ecosystem and seeks to harness the collective wisdom of its community members. By implementing a DAO, Polygon intends to involve stakeholders in shaping the future of their decentralized financial offerings. This move reflects a strategic shift towards inclusive decision-making and transparency, in line with the ethos of blockchain technology. The adoption of DAOs, exemplified by Polygon's efforts, brings several advantages. It democratizes decision-making, giving all participants a voice in shaping the organization.
However, DAO implementation is still in preliminary stages and faces challenges. Evolving regulations require clear guidelines for legal compliance. Technical aspects like scalability, smart contract security, and interoperability need careful management. Promoting awareness and overcoming the shift from centralized models to DAOs pose additional considerations. These are some basic challenges we just discussed above.
Polygon's pioneering DAO initiative in the Indian startup scene signifies a major leap towards transparency, collaboration, and innovation. Despite challenges, DAOs hold the potential to reshape decision-making processes and drive transformative change in India's blockchain landscape.
Blockchain Technology in different sectors of India
Blockchain technology has emerged as a disruptive force with the potential to transform various sectors of the Indian economy. By leveraging the decentralized, transparent, and secure nature of blockchain, these sectors can embrace innovative solutions to address specific challenges and drive economic growth in India. We can see how blockchain technology can be adopted in different sectors of India.
Banking sector
The banking sector in India can greatly benefit from blockchain technology. For instance, the collaboration between ICICI Bank and Emirates NBD Bank has facilitated cross-border remittances using blockchain-based platforms, resulting in faster and cost-effective transactions. By eliminating intermediaries and leveraging the decentralized nature of blockchain, such initiatives enhance financial inclusion and improve access to banking services for millions of Indians. Moreover, blockchain can enhance the security and efficiency of various banking operations, such as KYC (Know Your Customer) processes, trade finance, and supply chain finance.
Real Estate sector
In the Indian real estate sector, blockchain technology offers significant advantages in terms of transparency, efficiency, and security. One notable example is the partnership between IBSA and Tech Mahindra, which aims to develop a blockchain-based land registry system. This initiative streamlines property transactions, reduces fraud, and ensures transparent and tamper-proof land ownership records, thus instilling confidence among buyers, sellers, and investors. Additionally, blockchain can enable fractional ownership and enhance liquidity in real estate investments, allowing small investors to participate in the market.
= Healthcare sector
In the healthcare sector, blockchain technology presents transformative opportunities. A notable example is the collaboration between Apollo Hospitals and IIT Madras, which aims to leverage blockchain for secure storage and sharing of electronic health records (EHRs). By enabling patients to control access to their health data and ensuring interoperability among healthcare providers, blockchain-based EHR systems can improve healthcare outcomes, enhance patient privacy, and facilitate medical research. Moreover, blockchain can also be used for drug traceability, clinical trials management, and monitoring the supply chain of pharmaceutical products.
Government sector
The Indian government has recognized the potential of blockchain technology to improve transparency and efficiency in public services. For instance, the Telangana State Government has implemented a blockchain-based land records management system. This initiative digitizes land ownership records, reduces corruption, and disputes, and expedites property transactions. Similarly, the Maharashtra government is exploring the use of blockchain to digitize educational certificates, ensuring their authenticity, and reducing fraud. Additionally, blockchain can enhance the efficiency and transparency of government procurement processes, public welfare distribution, and identity management systems.
Agriculture sector
In the agricultural sector, blockchain can empower farmers and transform supply chain processes. For instance, Agri10x, a blockchain-based marketplace, connects farmers directly with buyers, eliminating intermediaries and ensuring fair prices for agricultural produce. Moreover, blockchain can enable the tracing of agricultural products from farm to fork, ensuring food safety and authenticity. Additionally, blockchain-based platforms can facilitate access to credit and insurance for farmers, enhancing their financial inclusion and resilience in the face of uncertainties.
Survey Analysis
Introduction to the Survey
This report presents the findings of a comprehensive survey conducted on 10 Indian-based companies operating in the field of blockchain technology. This survey aimed to gain valuable insights into the operations, sector focus, profitability, vested capital, and prospects of these organizations. As India emerges as a key player in the global blockchain landscape, understanding the specific characteristics and challenges faced by Indian companies in this field becomes crucial. By posing generic questions to representatives of these companies, we sought to obtain a deeper understanding of the current state of the blockchain industry in India and shed light on the opportunities and obstacles that these companies encounter. The data presented in this report has been collected through a survey conducted on Google Forms given to 22 employees from different companies operating in blockchain technology. We received 10 responses. In this research, I have made a financial analysis of the different companies and the sector they majorly operate in. In the end, I will discuss the current challenges and the future of these companies.
Focus of operation
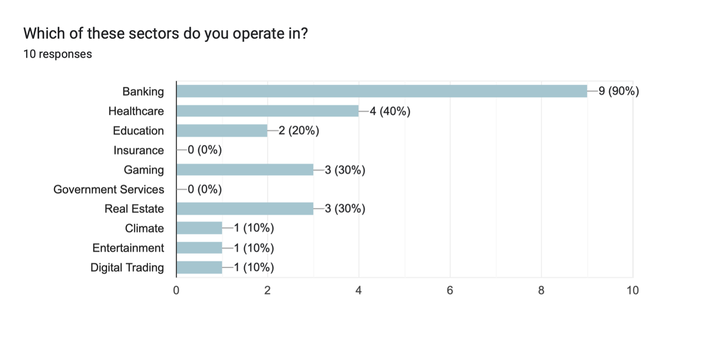
(Note to the graph: A company can give more than 1 answer)
Among the 10 India-based blockchain companies surveyed:
The banking sector is the most prominent, with 9 out of 10 companies operating within it. This suggests a strong focus on providing blockchain solutions for banking services, indicating the industry's recognition of the potential benefits of blockchain technology in financial transactions and security.
The healthcare sector follows, with 4 out of 10 companies operating within it. While not as prevalent as banking, it still demonstrates a significant interest in applying blockchain technology to improve healthcare systems, such as securing medical records or enhancing supply chain management.
Other sectors that show some presence include gaming, real estate, and education, with 3, 3, and 2 companies respectively. These sectors indicate a notable interest in leveraging blockchain technology to enhance gaming experiences, streamline real estate transactions, and improve educational processes.
There is no reported involvement in the insurance or government services sectors, suggesting that blockchain adoption in these areas may be limited or still in the early stages within the surveyed companies. This can be due to government banning the cryptography and restricting blockchain technology on a large scale. The climate, digital trading, and entertainment sectors each have one company operating within them. These sectors show a relatively minor but emerging presence of blockchain solutions, likely focused on sustainability efforts, digital asset trading, and entertainment-related applications.
Financial Analysis
The survey aimed to gather information on capital investment, profitability, investment in the previous fiscal year, and the percentage of revenue generated through blockchain-related operations. By delving into these financial indicators, we sought to understand the financial health and performance of these companies within the blockchain industry.
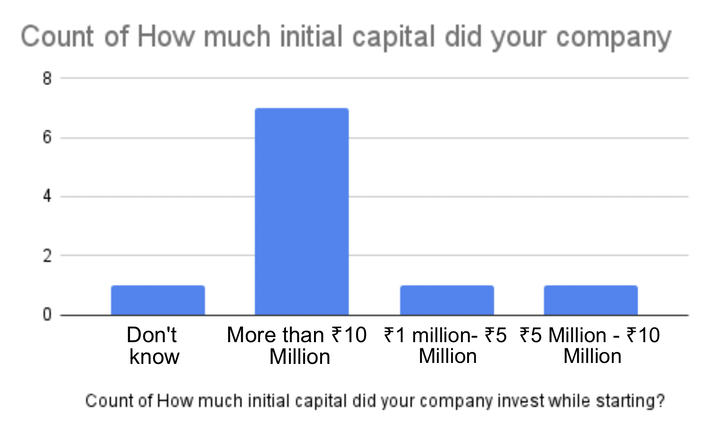
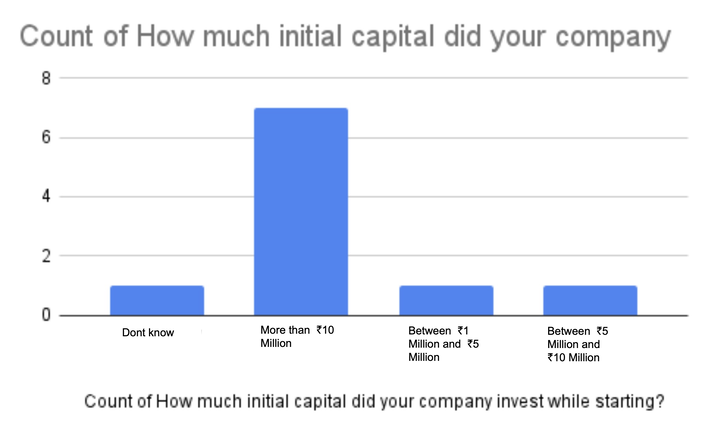
Among the participants from the 10 India-based blockchain companies surveyed, the majority (7 out of 10) reported investing more than 10 million rupees(estimated $122,000) as their initial capital. This signifies a significant financial commitment and highlights the resource-intensive nature of establishing and operating blockchain ventures.
The preference for investments exceeding 10 million(estimated $122,000) rupees can be attributed to several factors. Firstly, blockchain technology requires robust infrastructure, specialized talent, and extensive research and development efforts, which often necessitate substantial financial resources. Additionally, the absence of government aid or support specifically tailored for blockchain companies can contribute to the high setup costs. Without readily available financial assistance or incentives, these companies must rely on private funding sources to cover their initial capital requirements.
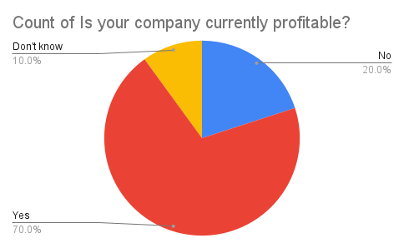
Among the participants from the 10 India-based blockchain companies surveyed, the responses varied regarding profitability:
• A majority of 7 individuals reported that their companies are profitable, indicating successful financial operations and business models. • 2 individuals mentioned that their companies are not profitable, suggesting ongoing challenges or early-stage development. • 1 person expressed uncertainty about the profitability status of their company, indicating a potential lack of financial visibility or involvement.
The specific responses can be influenced by several factors. Firstly, profitability in the blockchain industry can depend on various factors, including market demand, competition, cost management, and revenue streams. Companies that have successfully identified viable business models, secured clients, and effectively managed costs are more likely to report profitability. Furthermore, external factors such as regulatory challenges, market conditions, and the pace of blockchain adoption can also influence the profitability of these companies.
Overall, the analysis reveals a mixed picture of profitability among the surveyed companies, with a majority reporting profitability, while a minority are still striving to achieve positive financial outcomes.
Among the participants from the 10 India-based blockchain companies surveyed:
• 3 individuals mentioned that the investment in their companies was less than 1 million rupees(estimated. $12,200) in the last fiscal year. This indicates a relatively lower level of investment during that period. • 2 individuals reported investments between 1 million (estimated $12,200) and 5 million rupees (estimated $61,000), falling within a moderate investment range. • 2 individuals mentioned investments between 5 million(estimated $61,000) and 10 million rupees(estimated $122,000), representing a higher investment bracket. • 1 person stated that the investment was more than 10 million rupees (estimated $122,000) in the last fiscal year, indicating a significant financial infusion during that period. • 2 individuals expressed uncertainty about the amount of investment, suggesting a potential lack of awareness or involvement in the financial details of their companies.
The specific responses can be influenced by various factors. Firstly, the investment amount in the last fiscal year can depend on factors such as business growth, expansion plans, project requirements, and available funding sources. Companies with limited operations or early-stage development may require lesser investments compared to those in a growth phase or exploring ambitious projects.
Even though, the capital invested to maintain some of these companies is lower than the average of the companies in America, which is around $18,000. Meanwhile for some it is more.
The reason for low investment could be the cost of infrastructure and technology is relatively affordable. and India has a large pool of skilled developers and professionals available at competitive rates.The reason for high investment could be need for expensive hardware and software infrastructure, extensive research and development, compliance with regulatory frameworks, hiring top talent, and marketing efforts.
Summary of Financial Analysis
Most of the companies operated in the banking sector, which indicates a strategic alignment with the potential benefits of blockchain technology in enhancing financial services.
The sector's focus on banking, being resource-intensive, requires substantial initial capital investments. This aligns with the survey findings that revealed a majority of companies invested more than 10 million rupees as their initial capital. The high implementation costs are likely attributed to establishing robust infrastructure, acquiring specialized talent, and complying with regulatory frameworks.
However, despite the high implementation costs, the survey did not directly address the maintenance costs. It is worth noting that while implementation costs may be high, maintaining blockchain systems can be relatively cost-effective in the long run. Once the initial infrastructure is in place, ongoing maintenance costs can be comparatively lower, especially when considering the potential benefits of increased security, streamlined processes, and reduced intermediaries.
Therefore, although the cost of implementation may be high, the survey suggests that maintaining blockchain systems could be relatively cost-effective compared to traditional systems. This potential cost efficiency could be a contributing factor for companies choosing to invest in blockchain technology despite the initial capital outlay.
Overall, the interrelation between sector focus, initial capital investments, and maintenance costs emphasize the long-term financial considerations of implementing and maintaining blockchain systems, highlighting the potential cost-effectiveness in the maintenance phase.
Challenges
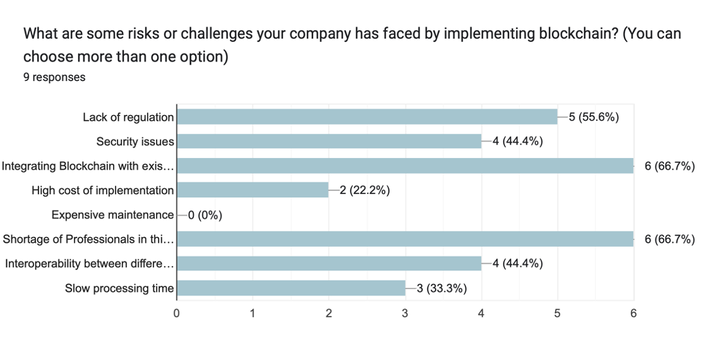
The responses provided by the surveyed India-based blockchain companies shed light on the specific risks and challenges they encountered during the implementation of blockchain technology. Analyzing these responses provides a deeper understanding of the hurdles faced by these companies and the areas that require attention.
Firstly, the lack of regulation was identified as a significant risk or challenge by 5 respondents. The absence of clear regulatory frameworks for blockchain technology creates uncertainty and can hinder the widespread adoption and integration of blockchain solutions. Companies operating in sectors such as banking, healthcare, and insurance, which are highly regulated, may face additional complexities in complying with existing regulations while leveraging the benefits of blockchain.
Security issues were a major concern for 4 participants. As blockchain implementations involve the storage and transfer of sensitive data, ensuring robust security measures is crucial. Cybersecurity threats such as hacking, unauthorized access, and data manipulation pose risks that need to be mitigated through strong encryption, access controls, and continuous monitoring of the blockchain network.
Integrating blockchain with existing systems was highlighted as a challenge by 2 respondents. The complexity of integrating blockchain technology with legacy infrastructure, databases, and processes can pose significant hurdles. It requires careful planning, coordination, and potentially making modifications to existing systems to ensure seamless integration and interoperability.
The high cost of implementation was mentioned as a challenge by 2 participants. The resource-intensive nature of implementing blockchain, including infrastructure setup, talent acquisition, and development efforts, can result in substantial financial investments. Balancing the initial costs with the long-term benefits and return on investment is crucial for companies considering blockchain adoption.
Interestingly, none of the respondents mentioned expensive maintenance as a significant risk or challenge. This indicates that once the initial implementation is complete, the ongoing maintenance costs of blockchain systems were not seen as a major concern. This may be attributed to the inherent advantages of blockchain, such as decentralized control, immutability, and self-auditing features, which reduce the need for expensive maintenance activities.
The shortage of professionals in the blockchain field was cited as a key challenge by 6 participants. The scarcity of skilled blockchain professionals can hinder the successful implementation and operation of blockchain projects. Companies may face difficulties in finding qualified personnel with expertise in blockchain technology, smart contracts, cryptography, and decentralized applications, potentially leading to delays or reduced efficiency.
Interoperability between different blockchain platforms was identified as a challenge by 4 respondents. The lack of standardized protocols and compatibility between various blockchain systems can hinder data sharing, collaboration, and the seamless transfer of assets across different platforms. Interoperability solutions, such as cross-chain bridges or standardized protocols, are needed to address this challenge and enable the full potential of blockchain technology.
Lastly, 3 participants mentioned slow processing time as a risk or challenge. Blockchain transactions can be slower compared to traditional centralized systems, especially when dealing with a large number of transactions or complex smart contracts. Optimizing transaction speeds and scalability without compromising security is an ongoing challenge in the blockchain space.
In conclusion, the in-depth analysis of the risks and challenges faced by the surveyed India-based blockchain companies highlights the importance of addressing regulatory uncertainties, security concerns, integration complexities, talent shortages, interoperability, and transaction speed to maximize the benefits and successful adoption of blockchain solutions. Overcoming these challenges requires a multi-faceted approach, including collaboration with regulatory bodies, robust security measures, careful integration planning, investment strategies, talent development, standardization efforts, and ongoing research and development in the blockchain ecosystem.
Summary of this survey
The findings indicate that the surveyed Indian companies are actively operating in sectors such as banking, healthcare, gaming, and real estate, showcasing a growing recognition of blockchain's potential across diverse industries. The significant initial capital investments made by several companies further emphasize the belief in the long-term value and impact of blockchain technology.
Despite the challenges identified, such as security issues, lack of regulation, integration complexities, and talent shortages, the future of blockchain in India appears promising. The Indian government has shown a proactive stance in exploring and embracing emerging technologies, including blockchain, by launching initiatives like the National Strategy on Blockchain and setting up blockchain sandboxes. This signifies a conducive environment for blockchain innovation and development in the country.
Moreover, India's vibrant startup ecosystem and the growing interest in blockchain technology among entrepreneurs and investors indicate a flourishing innovation landscape. Indian startups are exploring blockchain-based solutions in areas such as decentralized finance (DeFi), digital identity, intellectual property rights, and aggrotech, bringing forth new opportunities and disruptive business models.
Case Study of Spandan Technologies Pvt. Ltd.
Introduction
Spandan Technologies Pvt. Ltd., founded by Shreekant Kulkarni in July 2016 and headquartered in Pune, is a pioneering technology company at the forefront of India's digital transformation. With a relentless pursuit of cutting-edge technologies such as blockchain, the Metaverse, and WEB3.0, Spandan Technologies is driving innovation and reshaping the business landscape. This case study explores the remarkable journey of Spandan Technologies, focusing on its approach to technological advancements and its impact on India's digital economy.
Founding Inspiration
Spandan Technologies traces its roots to Shreekant Kulkarni's encounter with blockchain technology in 2016. Intrigued by the foundational principles of Bitcoin and its underlying blockchain technology, Kulkarni recognized its potential beyond cryptocurrencies. This realization ignited a passion to harness blockchain's power to address complex challenges and drive innovation across sectors in India.
Approach
Spandan Technologies takes an audacious approach, actively exploring uncharted territories to push the boundaries of technological innovation. The company's strategic vision revolves around embracing emerging technologies that hold the potential to disrupt industries and revolutionize business practices.
Spandan Technologies is a frontrunner in unlocking the transformative power of the Metaverse, a digital universe that transcends traditional boundaries. Through the establishment of Metaverse Experience Centers, engaging events, and innovative Metaverse Shops, the company enables businesses to explore new dimensions of immersive experiences. By pioneering the development of digital twin solutions, Spandan Technologies redefines concepts such as smart cities, governance, and digital tourism, opening unprecedented opportunities for businesses and governments alike.
They acquire blockchain to adapt finance, supply chain, and governance enabling businesses to adapt to the demands of the digital age.
Financial Analysis
Spandan Technology exhibited substantial growth in Fiscal years 2022 and 2023. Metaverse projects (A project under Spandan Technology regarding metaverse) generated $2734.66 in FY 2022, which increased to $6592.48 in FY 2023, indicating a growth rate of 141%. Blockchain projects contributed $3418.32 in FY 2022 and grew to $9375.97 in FY 2023, representing a remarkable growth rate of 174%. Training assignments showcased the highest revenue growth, reaching $4089.78 in FY 2022 and soaring to $19,899.51 in FY 2023, marking an extraordinary growth rate of 386%.
While expenses saw a significant increase, Spandan Technology managed them effectively. Equipment expenses rose from $598.21 in FY 2022 to $4639.15 in FY 2023, primarily due to investments in acquiring necessary equipment. Wages increased from $2563.74 to $10,254.96, reflecting the company's expansion and additional workforce. Travel expenses rose from $891.21 to $3161.95, likely driven by increased business travel.
The net profit for Spandan Technology improved substantially, reaching $4407.19 in FY 2022 and further rising to $11,000.00 in FY 2023. This indicates successful revenue growth, effective cost management, and enhanced profitability.
Now we will use ratios to understand it more clearly:
Revenue Growth Rate: The company experienced significant revenue growth across its segments. The revenue from metaverse projects grew at a rate of 141% ($2734.66 to $6592.48), while blockchain projects witnessed a growth rate of 174% ($3418.32 to $9375.97). Training assignments showcased exceptional growth, with a growth rate of 386% ($4089.78 to $19,899.51). These growth rates indicate the company's ability to expand its business and capture new opportunities.
Net Profit Margin: Spandan Technology effectively managed its expenses, as evidenced by the growth in net profit. The net profit margin improved from 43% ($4407.19) in FY 2022 to 31% ($11,000.00) in FY 2023. This indicates the company's ability to generate profits while efficiently controlling costs.
Summary
Based on the provided profit and loss statement, Spandan Technology has demonstrated remarkable revenue growth across its segments, showcasing its ability to capitalize on emerging opportunities in metaverse projects, blockchain projects, and training assignments. The company's effective cost management is evident from the improved net profit margin, indicating its ability to generate profits while controlling expenses.
With a healthy gross profit margin and operating profit margin, Spandan Technology displays a solid foundation in terms of profitability. Although there was a slight decrease in margins in FY 2023 compared to FY 2022, the company has maintained a positive trend overall.
Considering these financial indicators, the future of Spandan Technology appears promising. The significant revenue growth and improving profitability indicate the company's competitive strength and ability to adapt to market demands. To sustain this momentum, Spandan Technology should continue focusing on cost optimization, diversifying its revenue streams, and leveraging its expertise in metaverse projects and blockchain technology.
Furthermore, the company should stay attuned to industry trends and technological advancements to identify new growth avenues. With a strong financial position and a track record of success, Spandan Technology is well-positioned to seize opportunities in the evolving digital landscape and establish itself as a leading player in the Indian technology sector.
Conclusion
In conclusion, this research has provided valuable insights into the potential of blockchain technology in India. It has examined the concept of DAO status, the current status of blockchain and highlighted the success of Spandan Tech as an exemplar in the blockchain industry.
The analysis conducted in this paper has shown that granting DAO status in India can have significant implications. Recognizing DAOs as legal entities promotes transparency, accountability, and efficiency in decision-making processes. This legal recognition can foster innovation and encourage the growth of blockchain-based organizations, contributing to economic development in the country.
Furthermore, the future of blockchain in India appears promising. The government's initiatives, such as blockchain sandboxes and the "Digital India" campaign, demonstrate a commitment to creating a conducive environment for blockchain innovation. As more companies and organizations embrace blockchain technology, India is likely to experience significant growth in this field, leading to economic progress and technological advancements.
The success of Spandan Tech serves as an illustration of the tangible benefits that blockchain technology can offer. Through its implementation of blockchain solutions, Spandan Tech has achieved streamlined operations, cost reductions, and enhanced trust among stakeholders. This success story underscores the transformative potential of blockchain technology in revolutionizing traditional industries.
However, challenges such as regulatory frameworks, scalability, and interoperability need to be addressed to fully harness the potential of blockchain in India. Collaboration between government bodies, industry leaders, and academia is essential to establish clear guidelines, foster research and development, and facilitate the widespread adoption of blockchain technology.
In conclusion, this research has shown that the concept of DAO status and the success of companies like Spandan Tech exemplify the transformative power of blockchain technology in India. By embracing blockchain and creating an enabling environment, India can position itself as a global leader in blockchain innovation, driving economic growth and societal advancement in the years to come.
Bibliography
Takyar, Akash (2023). "How to determine the cost of blockchain implementation?"
Diwan, Pankaj (2023). "Role of Blockchain In India’s digital vision"
Bhagi, A., Banerjee, S., Sharma, N., Asthana, K., & Chowdhry, B. (2020). "Blockchain The India Strategy Part I"[Niti Aayog]
Mansur, Rishabh (2021). "India's first Decentralised Autonomous Organisation (DAO)"
Samanta, Sourish (2022). "What is a Decentralised Autonomous Organisation (DAO)?
Rakshit, S., Islam, N., Mondal, S., & Paul, T. (2022). "Influence of blockchain technology in SME internationalization: Evidence from high-tech SMEs in India." [Technovation],
Gupta, Vivek (2022). "Why higher adoption of blockchain is crucial to economic growth"